How does the spunmelt process differ from other nonwoven fabric manufacturing methods like needle punching or hydroentangling?
The spunmelt process is a unique method of producing nonwoven fabrics that combines both spunbond and melt-blown technologies, resulting in versatile and high-quality materials used in various applications, from medical supplies to everyday products like diapers and napkins. Unlike other nonwoven fabric manufacturing methods, such as needle punching or hydroentangling, spunmelt technology offers distinct advantages in terms of efficiency, fabric characteristics, and production capabilities.
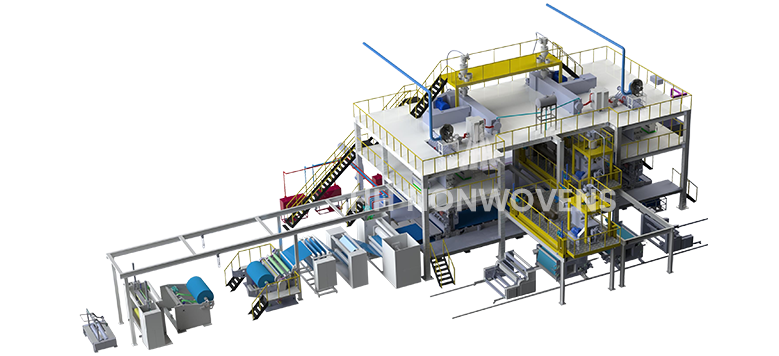
At the heart of the spunmelt process is its ability to produce fabrics using a combination of two processes: spunbonding, which involves extruding continuous filaments of thermoplastic polymer, and melt-blowing, which creates finer fibers by blowing molten polymer through high-velocity hot air. This dual functionality allows spunmelt machines to manufacture both spunbond and melt-blown fabrics simultaneously, thereby enhancing production flexibility and output efficiency. In contrast, needle punching and hydroentangling are mechanical bonding methods that require additional steps. Needle punching uses barbed needles to entangle fibers, while hydroentangling employs high-pressure water jets to achieve a similar result. Both methods tend to be more labor-intensive and slower, often requiring pre-made webs to be processed further, which can add to production costs and time.
The material properties of spunmelt fabrics also set them apart from those created through needle punching or hydroentangling. Spunmelt fabrics are generally lighter and can achieve higher strength with lower weights, making them ideal for applications that require both durability and comfort. The fine fibers produced in the melt-blown process provide excellent filtration capabilities, which are crucial for medical and hygiene products. In contrast, needle-punched fabrics typically have a thicker profile and may lack the same level of softness or filtration efficiency, while hydroentangled fabrics, though soft and drapable, often do not achieve the same strength-to-weight ratio as spunmelt materials.
Furthermore, the automation and advanced technology in spunmelt machines, such as those produced by Jiashan HH Nonwovens Machinery Co., Ltd., significantly enhance the operational ease and quality control of the manufacturing process. These machines often feature PLC controls and touch-screen interfaces, streamlining operations and allowing for quick adjustments to production parameters. In contrast, needle punching and hydroentangling processes may require more manual intervention and supervision, making them less efficient for high-volume production.
The spunmelt process differentiates itself from other nonwoven fabric manufacturing methods by combining the strengths of both spunbond and melt-blown technologies, resulting in efficient production, superior fabric properties, and reduced operational complexity. As industries continue to demand high-performance materials for a variety of applications, the spunmelt process is likely to play a significant role in meeting these needs while remaining competitive in the evolving landscape of nonwoven fabric manufacturing.







 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى





